In today’s data-driven world, having an effective data management strategy is crucial for organizations looking to leverage their data to its fullest potential. Implementing industry best practices can help streamline this process, ensuring that data is not only accessible but also of high quality and actionable. One such framework that provides a comprehensive approach to data management is the Data Management Capability Assessment Model (DCAM).
Understanding DCAM: A Layered Approach to Data Management
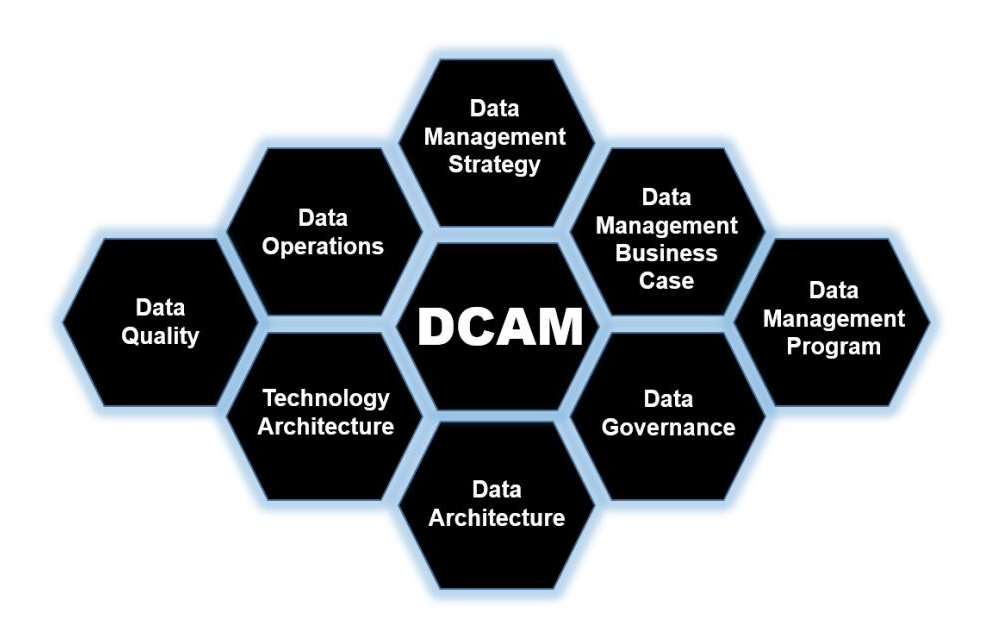
DCAM offers a structured methodology for managing data, emphasizing the importance of a layered approach to extract maximum value. This approach ensures that each aspect of data management is addressed systematically and effectively.
- Foundational Layer: Data Strategy and Business Case
- At the core of any data management initiative is a well-defined data strategy. This involves setting clear objectives and understanding the business case for managing data. It ensures that there is a strategic direction and a solid rationale for investing in data management practices.
- Additionally, establishing a data management program and securing funding are critical steps. Without financial backing and a structured program, even the best strategies can falter.
- Execution Layer: Architecture and Quality Management
- Business and Data Architecture: This involves mapping out how data flows within the organization and how it supports business processes. A well-architected data environment is crucial for ensuring that data is available where and when it is needed.
- Data and Technology Architecture: This layer focuses on the technical infrastructure that supports data management. It includes databases, data warehouses, data lakes, and the technology stack that enables data processing and storage.
- Data Quality Management: Ensuring data quality is critical. This involves setting up processes and systems to monitor, clean, and maintain data to ensure it is accurate, complete, and reliable.
- Data Governance: Overarching these elements is data governance, which establishes policies, procedures, and standards to manage data effectively and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Collaboration Layer: Data Control Environment
- At this level, the focus is on creating a collaborative environment where data management practices are consistently applied and controlled. This involves fostering a culture of data stewardship and ensuring that everyone in the organization understands their role in managing data responsibly.
- Application Layer: Analytics Management
- Finally, at the application layer, the focus shifts to analytics management. This involves leveraging data to generate insights and support decision-making. Effective analytics management ensures that data is used to its fullest potential, driving business value and competitive advantage.
The Importance of Context and Mapping
A successful data management strategy begins with appropriately setting the context and defining what you want to achieve. Without this, it is impossible to map out or architect your data management stacks effectively. The foundational elements of strategy and business case must align with the execution and application layers to ensure coherence and effectiveness.
Why is data governance so important?
Data governance is a critical component of the data management framework, serving as the foundation for ensuring data quality, security, and compliance. It involves establishing a set of policies, procedures, and standards to manage data effectively across the organization. The key roles are:
- Data Owners: These individuals or teams are responsible for the data’s overall quality, integrity, and security. They make decisions about who can access the data and how it should be used. Data owners ensure that data management practices align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Data Stewards: Data stewards are tasked with overseeing the day-to-day management of data. They work closely with data owners to implement data governance policies and ensure data is accurate, accessible, and protected. Stewards often act as the bridge between IT and business units, facilitating communication and understanding.
- Data Custodians: Typically part of the IT department, data custodians are responsible for the technical aspects of data management. This includes data storage, maintenance, and protection. They ensure that the infrastructure and tools used to manage data are robust and secure.
- Data Governance Board/Committee: This is a governing body that includes data owners, stewards, custodians, and other key stakeholders. The council establishes and enforces data governance policies, sets priorities, and resolves conflicts related to data management.
Key elements of a data governance program include:
- Policy Development: Creating policies that define how data should be managed, accessed, and used. This includes data classification policies, data access policies, and data retention policies.
- Standards and Procedures: Developing standards and procedures to ensure consistency in data management practices across the organization. This includes data entry standards, data quality standards, and procedures for data correction.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Ensuring that data management practices comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulatory requirements. Risk management involves identifying potential data risks and implementing measures to mitigate them. Already discussed the approach to risk management in one of my previous articles.
- Training and Awareness: Providing training and resources to employees to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities in data governance. This helps create a culture of data stewardship across the organization.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing tools and processes to monitor data quality and governance practices. Regular reporting helps track compliance, identify issues, and measure the effectiveness of data governance initiatives. Remember this is where the funding aspect helps!
Consequences of Poor Data Management
Failing to set a proper context and map your data management processes can lead to several issues:
- Poor Data Quality: Without quality gateways, data can become inaccurate and unreliable, leading to poor decision-making.
- Inability to Action Data: Without appropriate governance and a well-architected data environment, organizations struggle to leverage their data effectively.
- Increased Costs: Poor data management can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs associated with data correction and management.
- Regulatory Risks: Non-compliance with data governance standards can result in legal and financial penalties.
- Lost Opportunities: Inaccurate or inaccessible data can prevent organizations from identifying and capitalizing on business opportunities.
In conclusion, implementing a data management strategy based on industry best practices like DCAM can help organizations unlock the full potential of their data. By addressing each layer of data management systematically, organizations can ensure that their data is of high quality, well-governed, and actionable, driving business value and success.
Thank you for reading this and as always, if you like the article please do not hesitate to share with your network.
Leave a comment