1. What is ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It is a critical compliance mechanism for organizations, providing a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information to ensure it remains secure. Adopting ISO 27001 is often a prerequisite for gaining new business as it demonstrates a commitment to protecting information assets.
An ISMS, as outlined by ISO 27001, is a comprehensive framework of policies and procedures. This framework includes all legal, physical, and technical controls involved in an organization’s information risk management processes. By implementing an ISMS, organizations can systematically identify, manage, and reduce risks to their information assets, thereby enhancing overall security posture and ensuring compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements.
Steps to Implement ISO 27001:
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Evaluate the current security posture against the ISO 27001 requirements to identify gaps.
- Scope the ISMS: Determine the boundaries of your ISMS, deciding which parts of the organization will be covered.
- Initiate High-Level Policy Development: Develop essential policies that provide a high-level framework for the ISMS.
- Perform a Risk Assessment: Identify and evaluate security risks to your information assets.
- Select and Apply Controls: Choose appropriate controls from ISO 27001 Annex A to mitigate identified risks.
- Develop Risk Documentation: Document the risk assessment and risk treatment plans.
- Conduct Staff Awareness Training: Train employees on information security policies and procedures.
- Assess, Review, and Conduct an Internal Audit: Regularly review the ISMS and perform internal audits to ensure compliance.
- Opt for a Certification Audit: Undergo a certification audit by an external body to achieve ISO 27001 certification.
ISO 27001:2022: The updated ISO 27001:2022 standard includes 93 controls, organized into 4 themes:
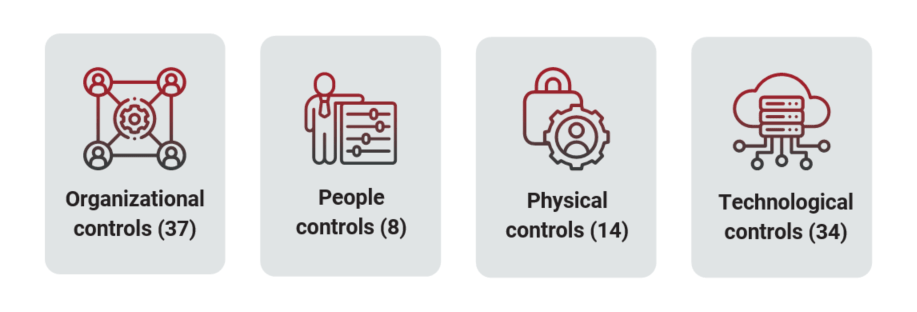
- People Controls: Focus on the human aspect of information security, such as training and awareness.
- Physical Controls: Address physical access and environmental security.
- Technology Controls: Cover the technical measures like firewalls and encryption.
- Organizational Controls: Encompass policies, procedures, and governance structures.
ISO 27002: provides guidelines for the implementation of controls listed in ISO 27001 Annex A. It serves as a practical guide to help organizations select and implement the necessary controls to meet the requirements of ISO 27001.
2. The Lifecycle of ISO 27001

The lifecycle of ISO 27001 implementation involves several key stages:
Gap Analysis (Pre-Assessment):
- Objective: Identify the gaps between current practices and ISO 27001 requirements.
- Process: Can be performed internally by assessing existing controls and procedures.
Design Review (Stage 1):
- Objective: Develop and review the ISMS design to ensure it meets the necessary requirements.
- Process: Focus on high-level policy development and selecting appropriate controls.
Certification Audit (Stage 2):
- Objective: Achieve certification from an accredited issuing body.
- Process: Conducted by an external auditor who verifies the ISMS against ISO 27001 standards.
Surveillance Audits:
- Year 1 and Year 2: Conducted annually to ensure ongoing compliance and to address any issues.
- Objective: Maintain certification by demonstrating continuous improvement and adherence to the ISMS.
Recertification Audit:
- Year 3: A comprehensive audit to renew the certification.
- Objective: Ensure the ISMS remains effective and compliant with ISO 27001 standards.
3. Implementation Challenges and Strategies
Implementing ISO 27001 can be challenging, but adopting an audit mentality can help:
- Audit Mentality: Approach the implementation with a risk based mindset focused on continuous improvement and compliance.
- ISO 27002 Guide: Use ISO 27002 to guide the practical implementation of controls, ensuring both design and operational effectiveness.
- Design Effectiveness: Ensure the control design adequately covers the necessary security requirements.
- Operational Effectiveness: Verify that the controls are implemented correctly and function as intended.
4. Using ISO 27001 for Cybersecurity Maturity Assessment
ISO 27001 can also be leveraged as a tool for assessing cybersecurity maturity:
- Gap Identification: Identify deficiencies and gaps in the current cybersecurity posture.
- Strategic Planning: Use the findings to inform your cybersecurity strategy, investment decisions, and budgeting.
- Weighted Scoring: Assign weights to controls based on their importance to your organization and industry challenges.
- Annual Testing: Test all controls annually to ensure they remain effective.
- Project Management: Establish a testing schedule and manage it like a project to ensure thorough coverage and timely completion.
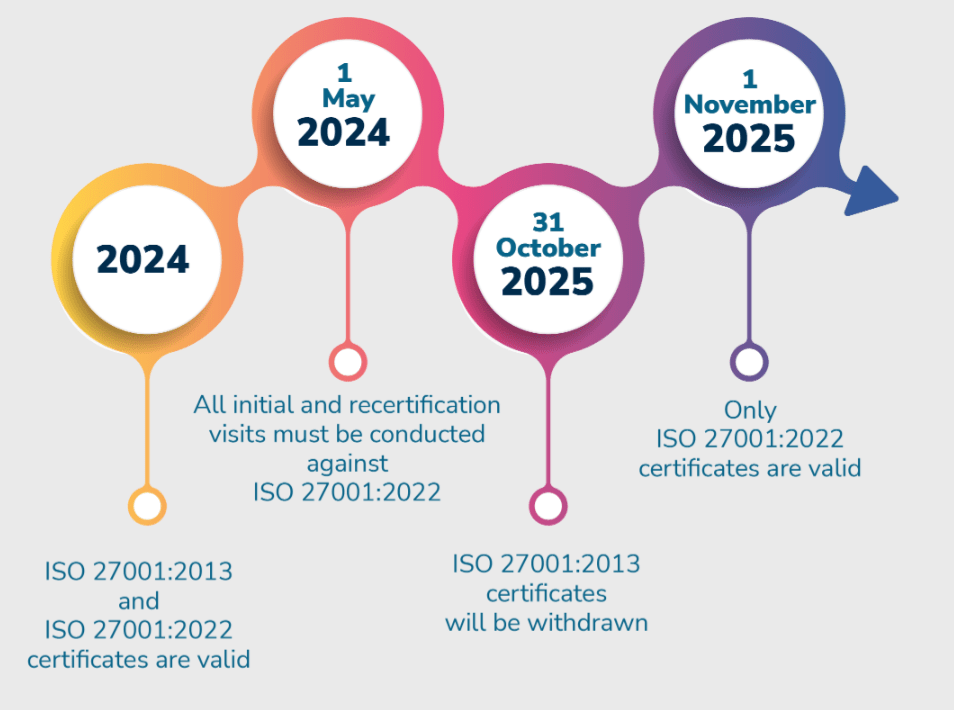
Transitioning from ISO27001:2013 to 2022
Transitioning from ISO 27001:2013 to ISO 27001:2022 involves several key steps to ensure that your Information Security Management System (ISMS) is updated to meet the new requirements. The updated standard introduces new controls and re-organizes existing ones to better address modern information security challenges.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis:
- Compare your current ISMS against the requirements of ISO 27001:2022.
- Identify areas where your current controls may need to be updated or new controls need to be implemented.
- Understand the New Controls:
- ISO 27001:2022 introduces 11 new controls, which are organized under the previously mentioned themes:
- Organizational Controls:
- Threat intelligence
- Information security for the use of cloud services
- ICT readiness for business continuity
- Physical Controls:
- Physical security monitoring
- Technological Controls:
- Configuration management
- Information deletion
- Data masking
- Data leakage prevention
- Monitoring activities
- Web filtering
- Secure coding
- Organizational Controls:
- ISO 27001:2022 introduces 11 new controls, which are organized under the previously mentioned themes:
- Re-organize Existing Controls:
- The 2022 version re-organizes the 93 controls into four themes: Organizational, People, Physical, and Technological. Review and map your existing controls to the new structure.
- Update your documentation to reflect the new control structure.
- Update Risk Assessments and Treatment Plans:
- Incorporate the new controls into your risk assessment process.
- Update your risk treatment plans to include measures for addressing any newly identified risks.
Conclusion
Implementing ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 involves a structured approach to managing information security. By following the lifecycle stages—gap analysis, design review, certification audit, surveillance audits, and recertification—you can ensure a robust ISMS. Embracing an audit mentality, leveraging ISO 27002 for control implementation, and using ISO 27001 for cybersecurity maturity assessments will help maintain a high level of security and compliance. Regular testing and strategic planning based on identified gaps will further strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity posture.

Leave a comment